Serial Device Servers for Smart Manufacturing: A 2025 Trend Analysis
In the age of Industry 4.0 and moving towards Industry 5.0, smart manufacturing relies on seamless connectivity between legacy equipment and modern digital systems. For factories with decades-old serial-based machinery, the serial device server, also known as a serial-to-Ethernet converter or serial-over-IP gateway, has become a critical bridge.
In 2025, the role of serial device servers is transforming, shaped by trends in IIoT, edge computing, cybersecurity, and AI-driven operations. This blog explores how serial device servers are evolving, why they remain relevant, and what manufacturers should know to stay ahead.
1. Market Landscape and Growth Forecasts
- The global serial device server market is expected to cross 300 million USD in 2025, with steady growth through the next decade.
- Growth is driven by the need to modernize legacy equipment, expand IIoT integration, and enable secure, remote data access.
- Asia-Pacific is leading adoption due to industrial expansion, while Europe and North America see strong retrofit demand in existing plants.
2. Why Serial Device Servers Still Matter in Smart Manufacturing
Many assume “everything is Ethernet now,” but factories still rely heavily on machines with RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485 interfaces. Replacing these machines is costly and disruptive.
A serial device server allows:
- Legacy devices to connect with SCADA, MES, and cloud platforms
- Protocol flexibility for Modbus RTU, proprietary protocols, and custom setups
- Secure and centralized remote monitoring
- Reduced downtime and extended hardware life
Instead of ripping and replacing, manufacturers can use serial device servers to integrate old and new seamlessly.
3. 2025 Trends in Serial Device Servers
Edge-First Capabilities
Modern device servers process data locally, filtering, compressing, and sending only critical insights. This reduces network load and improves responsiveness.
IT and OT Convergence
Device servers are no longer just converters. They integrate with IT networks, supporting SNMP, REST APIs, OPC UA, and other standards, enabling true IT/OT unification.
Cybersecurity as a Core Feature
With increased connectivity comes risk. Device servers in 2025 emphasize encrypted communication, secure boot, and role-based access aligned with industrial security standards.
Multi-Connectivity Options
Wired Ethernet remains common, but newer models support Wi-Fi, LTE, and even private 5G. This is crucial for modular or mobile manufacturing environments.
Software-Defined Networking
Some device servers now support virtualization, dynamic routing rules, and containerized applications, adding flexibility to network configurations.
AI and Predictive Maintenance
Edge AI modules in device servers can detect anomalies and trigger alerts before failures occur, enabling predictive maintenance strategies.
Sustainability and Longevity
By extending the life of machines through connectivity, serial device servers help reduce e-waste and support cost-effective, sustainable operations.
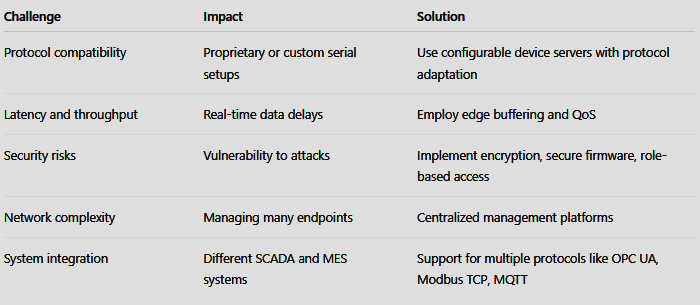
4. Challenges and Solutions
5. Use Cases in Smart Manufacturing
Retrofitting Legacy Systems
Factories can connect older PLCs and sensors to modern MES systems without replacing equipment.
Remote Monitoring
Serial device servers with wireless connectivity allow real-time monitoring of remote plants where Ethernet is impractical.
Modular Manufacturing
Mobile production cells can be networked quickly using wireless or hybrid device servers.
Edge Filtering
Device servers filter or preprocess data, sending only valuable information to higher-level systems.
Predictive Maintenance
Data from sensors is fed through serial device servers into analytics systems, helping predict failures and optimize uptime.
6. How Avyanna Tech Aligns with 2025 Needs
Avyanna Tech’s serial-to-Ethernet converters are designed for the demands of modern industrial environments. Key features include:
- Support for RS-232/422/485 and Modbus RTU
- Edge-enabled data filtering and lightweight scripting
- Multi-connectivity with Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and cellular options
- Advanced security with secure boot, firmware validation, and encrypted communication
- Centralized management with remote updates and monitoring
- Expert support for integrating with MES, ERP, and cloud platforms
These solutions empower manufacturers to extend hardware life, improve efficiency, and ensure secure connectivity in smart factories.
7. SEO, SXO, and AEO Optimization Highlights
- Keyword placement: The term serial device server and its variants appear naturally across titles, headers, and content.
- Search experience: Content answers key user questions, includes comparison tables, and provides clear CTAs.
- Answer engine optimization: Structured sections, FAQs, and clear entity references improve visibility in AI-driven summaries.
- Semantic richness: Related terms like IIoT, edge computing, OPC UA, predictive maintenance, and Industry 4.0 reinforce topical authority.
8. FAQs
What is a serial device server?
A serial device server is a device that enables serial-based equipment (RS-232, RS-422, RS-485) to communicate over Ethernet or IP networks.
Why use a serial device server in smart manufacturing?
It allows legacy machines to connect with modern IIoT and cloud systems without costly replacement.
What features should a 2025-ready device server include?
Multi-protocol support, cybersecurity, edge processing, wireless options, and centralized management.
Can device servers handle data locally?
Yes, many include edge logic for preprocessing and event filtering.
How do I choose between wired and wireless device servers?
Wired is ideal for fixed installations, while wireless offers flexibility for mobile or remote environments.
Conclusion
Smart manufacturing in 2025 demands both innovation and practicality. The serial device server remains a vital tool for bridging legacy systems with modern digital platforms, enabling predictive maintenance, sustainable operations, and secure connectivity.
Avyanna Tech’s solutions are built to support this transformation, helping factories future-proof their operations while maintaining efficiency and safety.






[email protected]